1. Market Forces
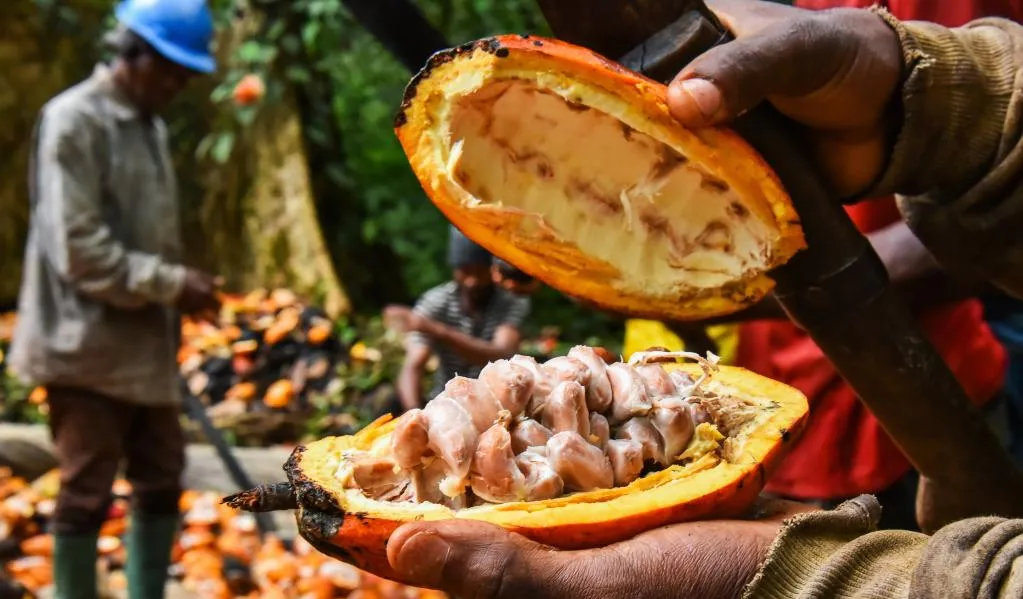
According to Warren Patterson, an analyst at ING, cocoa was the top-performing commodity in 2024 - and prices are likely to remain high. It closed out the year ahead of every major commodity after months of poor weather and weak harvests sparked a triple-digit gain for the crop.
Cocoa gained approximately 172% in the past year, briefly reaching a record of nearly $13,000 per metric ton on the ICE international exchange in December. According to a report on businessinsider, prices have appreciated dramatically as leading cocoa-producing countries, Ghana and Cote d’Ivoire, have been hit by crop failures. Pod disease, floods, and falling pay for farmers all contributed to a worsening supply crunch.
In the short term, the cocoa outlook is bullish due to weather concerns, reduced crop forecast, funds participation, and low warehouse stocks despite being replenished by the main crop. In the long term, cocoa outlook is still bullish due to low stocks, the risk of funds re-entering, and resilient demand.
2. Climate Change and Crop Yields
Cocoa cultivation heavily depends on specific climatic conditions, requiring consistent rainfall and temperatures between 20°C and 30°C. By 2025, cocoa-growing regions may see further shifts in suitable growing zones, pushing farmers to higher altitudes or requiring investments in drought-resistant cocoa varieties. Still, these adaptations come with significant costs and technological hurdles, which the industry must address.
3. Macroeconomics
A 2024 report from the International Cocoa Organization (ICCO) revealed that around 81% of Ghana’s cocoa-producing area has become affected by Cocoa Swollen Shoot Disease (CSSVD). The region covers about 410,229 hectares, with 330,456 hectares infected.
Climate change is exacerbating the crisis, creating favourable conditions for spreading such threats. It has forced Ghana to cut its cocoa harvest forecast again this season.
Following the latest data, the world’s second-largest grower has trimmed its outlook for the season that began in September by 5%. Predictions are now for a harvest of approximately 617,500 tons after the country lowered its crop expectation by 20% to 650,000 tons in August last year.
Cote d’Ivoire cocoa exporters also fear a drop in supplies after poor weather in December, exacerbated by the impact of El Niño and insufficient recovery for the crop. ‘’Cocoa farmers in Ivory Coast are expecting smaller harvest volumes in February and March,’’ an analyst at Commerzbank Research said.
The industry must invest in research to develop resistant cocoa strains and integrate pest management strategies. By 2025, biotechnology and precision agriculture could be more prominent in addressing these issues.
4. Economic Pressures on Smallholder Farmers
Volatile cocoa prices, exacerbated by global economic uncertainties, make it difficult for farmers to achieve financial stability. Most of the world’s cocoa is produced by smallholder farmers, many of whom live below the poverty line.
Fairtrade initiatives, direct trade models, and government interventions in West Africa's leading producer countries are essential for addressing this imbalance. In 2025, consumer pressure for ethically sourced cocoa will likely intensify, urging companies to ensure fair wages and better working conditions for farmers.
5. Sustainability and Deforestation
As global awareness grows of deforestation’s role in biodiversity loss and climate change, stakeholders are pushing for more sustainable farming practices.
Compliance with deforestation-free certification standards, such as those proposed by the delayed European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), will become increasingly important in 2025. Companies must invest in traceability systems and collaborate with local governments to promote agroforestry and reforestation efforts.

Despite the postponement, companies are advised to utilize this additional time to prepare for compliance by:
• Mapping Supply Chains: Identify and document the origins of commodities to ensure they meet the EUDR’s deforestation-free criteria.
• Implementing Monitoring Systems: Adopt satellite monitoring and geolocation tracking technologies to oversee supply chain activities effectively.
• Engaging with Suppliers: Collaborate with suppliers to ensure adherence to sustainable practices and gather necessary compliance data.
6. Child Labour and Ethical Concerns
Child labour remains a persistent issue in the cocoa industry, particularly in West Africa. Despite efforts to address this problem, estimates suggest that over 1.5 million children are still involved in hazardous cocoa farming activities.
Stricter regulations and consumer demand for ethical practices will likely pressure companies to enhance transparency and accountability in their supply chains by 2025. Blockchain technology and third-party audits may become vital tools for ensuring compliance with labour standards.
7. Market Diversification and Consumer Trends
The cocoa market faces challenges from changing consumer preferences. Plant-based and health-conscious products are rising, with many consumers seeking alternatives to traditional milk chocolate. The growing demand for single-origin and artisanal chocolates is also reshaping the industry.
In 2025, companies must adapt by diversifying their product portfolios, investing in marketing campaigns highlighting sustainable and ethical practices, and tapping into niche markets.
8. Emerging Trend in Lab-Based Chocolate
Lab-based chocolate production is experiencing significant advancements to address sustainability challenges and meet evolving consumer preferences.
Innovative companies like California Cultured are developing chocolate by cultivating cacao plant cells in controlled environments, eliminating the need for traditional farming.
This method involves extracting cells from cacao trees and nurturing them in bioreactors to produce cocoa solids and butter. Companies are pioneering this technology to create non-GMO chocolate, reducing environmental impacts and ensuring a consistent supply.
Official: The Top 10 Most Influential People in Cocoa & Chocolate 2024

It's the list the industry has been waiting for. Have we missed anyone? Subscribe to see the results and give your opinion and feedback